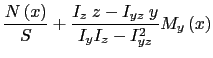 |
(10.1) | ||
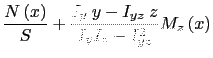 |
(10.2) |
Las distribuciones de tensiones normales para el momento actuando según el eje y o el eje z son, respectivamente
En la Figura 10.1 se muestra la distribución de tensiones en una sección sometida a flexión compuesta según el eje y.
Si los ejes son principales de inercia, las expresiones (10.1) y (10.2) se simplifican: